In a world where technology is reshaping every aspect of our lives, the healthcare industry is no exception. Telemedicine, once a futuristic concept, has swiftly become a cornerstone of modern healthcare delivery. The convenience of consulting with healthcare professionals from the comfort of our homes has transformed patient care, making it more accessible and efficient. However, as with all technological advancements, telemedicine brings with it a host of new challenges and risks, particularly in the realm of cybersecurity. 🛡️
Imagine sharing your most intimate health concerns with your doctor through a digital platform, only to find out that your sensitive information has been compromised. This is not just a hypothetical scenario; it’s a reality faced by many as cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated. The very platforms that promise safety and confidentiality in healthcare must be fortified against these digital threats. This article delves into the critical importance of cybersecurity in telemedicine platforms, highlighting the need for robust security measures to protect your virtual health.
As we navigate this digital healthcare landscape, understanding the intersection of telemedicine and cybersecurity is crucial. We will explore the potential vulnerabilities within telemedicine platforms and the various forms of cyber threats that target them. From data breaches to ransomware attacks, these threats not only jeopardize patient privacy but also undermine the trust in digital healthcare solutions. 🔐
But fear not, as this article isn’t just about identifying problems. We aim to provide actionable insights into how both providers and patients can enhance their cybersecurity measures. By the end of this piece, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of the best practices for safeguarding personal health information in the digital age.
The rise of telemedicine has been meteoric, fueled in part by the global health crises that have necessitated remote healthcare solutions. This rapid adoption has unfortunately outpaced the implementation of adequate security protocols, leaving many systems vulnerable. In our exploration, we’ll discuss the current state of cybersecurity in telemedicine, analyzing real-world case studies to illustrate both the consequences of security lapses and the strategies that have proven effective in mitigating these risks.
Moreover, we will delve into the regulatory landscape, examining the role of policies such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in shaping the security standards for telemedicine platforms. Understanding these regulations is essential for healthcare providers to remain compliant and for patients to know their rights and protections.
Technology is evolving at a breakneck pace, and with it, the tactics employed by cybercriminals. This article will introduce you to the latest advancements in cybersecurity technology that are being leveraged to protect telemedicine services. From encryption techniques to blockchain applications, these innovations are paving the way for a more secure digital healthcare environment.
Lastly, we will emphasize the shared responsibility in maintaining cybersecurity. While healthcare providers must invest in cutting-edge security technologies, patients also play a critical role. Simple practices such as using strong passwords, being vigilant about phishing attempts, and ensuring secure network connections can significantly enhance personal cybersecurity. 🖥️
In conclusion, as telemedicine continues to revolutionize the healthcare industry, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. By understanding the risks and adopting proactive measures, we can ensure that the benefits of digital healthcare are realized without compromising on security. Join us as we unravel the complexities of cybersecurity in telemedicine, providing you with the knowledge and tools to protect your virtual health in an increasingly digital world.
# Safeguarding Your Virtual Health: The Crucial Role of Cybersecurity in Telemedicine Platforms
As technology rapidly advances, the healthcare industry is embracing digital transformation at an unprecedented rate. One of the most impactful innovations in recent years is telemedicine. This technology allows patients to access healthcare services remotely, offering convenience, efficiency, and often, quicker access to medical professionals. However, with the growth of telemedicine comes a new set of challenges, notably the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient data. In this article, we’ll delve into the importance of cybersecurity in telemedicine platforms, exploring the risks, solutions, and best practices to ensure the safety and privacy of virtual healthcare.
## Understanding the Risks: Why Cybersecurity Matters in Telemedicine
In the digital age, data breaches and cyberattacks have become increasingly common, targeting sectors across the board. The healthcare industry, however, stands as one of the most attractive targets for cybercriminals due to the sensitive nature of the data it handles. Patient records contain not only medical information but also personal and financial details that, if compromised, can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and serious privacy violations.
Telemedicine platforms, by their very nature, collect and transmit large volumes of such sensitive information. This makes them particularly vulnerable to cyber threats. A breach in a telemedicine platform could expose data such as medical histories, diagnoses, treatments, and even real-time conversations between doctors and patients. The consequences of such breaches are severe, ranging from loss of patient trust to legal and financial repercussions for healthcare providers.
### Common Cyber Threats to Telemedicine Platforms
1. **Data Breaches**: Unauthorized access to patient data can result in sensitive information being leaked or stolen. Cybercriminals may sell this information on the dark web or use it for fraudulent activities.
2. **Ransomware Attacks**: These involve malware that encrypts files, rendering them inaccessible. Hackers then demand a ransom to unlock the data. For telemedicine platforms, this could disrupt services and compromise patient care.
3. **Phishing Attacks**: These attacks typically involve emails or messages that appear legitimate but are designed to trick individuals into providing personal information, such as login credentials.
4. **Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks**: During data transmission between the user and the server, hackers can intercept and potentially alter the data being communicated.
### The Human Element: A Key Vulnerability
While technology and systems can have vulnerabilities, the human element often presents the greatest risk in cybersecurity. Employees may inadvertently fall victim to phishing schemes, or use weak passwords that are easily compromised. Training healthcare providers and staff on recognizing cyber threats and practicing good cyber hygiene is crucial in mitigating risks.
**Call to Action**: Watch this video to understand more about the cybersecurity threats facing healthcare today: [Cybersecurity in Healthcare](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N0oZ9QuA4o).
## Building a Fortress: Strategies for Strengthening Cybersecurity in Telemedicine
Given the high stakes, healthcare providers must take a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Implementing a comprehensive strategy that encompasses technology, processes, and people is essential in safeguarding telemedicine platforms.
### Embracing Advanced Technologies for Security
To counter the evolving landscape of cyber threats, telemedicine platforms need to leverage advanced technologies that provide robust security measures.
– **Encryption**: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is fundamental. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it remains unreadable and unusable to anyone but the intended recipient.
– **Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)**: Requiring more than just a password to access sensitive information adds an additional layer of security. MFA can include factors such as biometrics, OTPs (one-time passwords), or security tokens.
– **Firewall and Antivirus Software**: These tools serve as the first line of defense against unauthorized access and malware. Regular updates and patches are critical to maintaining their effectiveness.
– **AI and Machine Learning**: Implementing AI-driven security solutions can enhance threat detection and response times. These technologies can analyze patterns and detect anomalies that might indicate a cyber threat.
### Best Practices for Healthcare Providers
Beyond technology, healthcare providers must adopt best practices to enhance cybersecurity in telemedicine platforms.
– **Regular Audits and Assessments**: Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and address them before they can be exploited. This includes reviewing access controls, network security, and incident response plans.
– **Data Minimization**: Limiting the amount of data collected and stored reduces the risk of exposure in the event of a breach. Providers should ensure they only collect information that is absolutely necessary for patient care.
– **Employee Training and Awareness**: Cybersecurity is everyone’s responsibility. Regular training sessions should be conducted to educate staff on recognizing and responding to cyber threats.
### Regulatory Compliance: A Critical Component
Compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S., and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU, is non-negotiable for telemedicine platforms. These regulations mandate stringent data protection measures, and non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal consequences.
| Regulation | Region | Key Focus |
| HIPAA | United States | Protects patient privacy and data security |
| GDPR | European Union | Regulates data protection and privacy for individuals |
**Call to Action**: For more insights on implementing cybersecurity measures, check out this informative guide on cybersecurity best practices in healthcare.
## Navigating the Future: Trends and Innovations in Cybersecurity for Telemedicine
As telemedicine continues to evolve, so too must the cybersecurity measures that protect it. Staying ahead of emerging threats requires continuous innovation and adaptation. Let’s explore some of the trends and innovations shaping the future of cybersecurity in telemedicine.
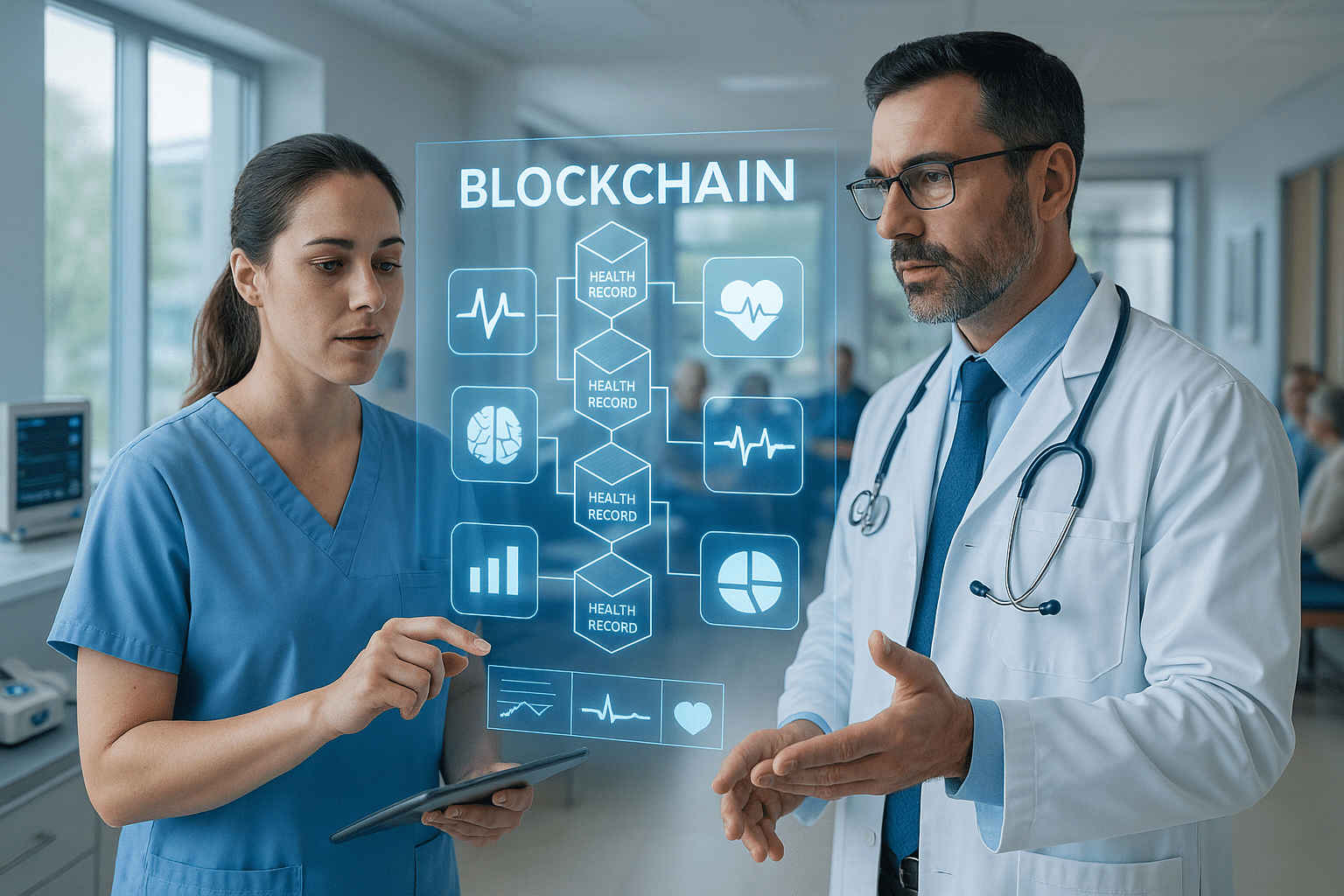
### The Rise of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, originally designed for cryptocurrency, is gaining traction in the healthcare industry for its potential to enhance data security and integrity. Blockchain’s decentralized nature means data is stored across multiple locations, reducing the risk of a single point of failure or attack. Additionally, its transparency and immutability make it an attractive solution for securing patient data and ensuring data accuracy.
### Zero Trust Architecture: Trust No One
The zero trust security model operates on the principle that no entity, whether inside or outside the organization, should be trusted by default. Instead, verification is required for every request to access resources. For telemedicine platforms, adopting a zero trust approach means implementing strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and validating user identities at every interaction.
### Telemedicine and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The integration of telemedicine with IoMT devices such as wearable health monitors and smart medical equipment presents new cybersecurity challenges. Protecting these interconnected devices from cyber threats is essential to ensuring patient safety and data privacy. This involves securing device communication channels, regularly updating firmware, and implementing network segmentation to isolate medical devices from other networked systems.
### The Role of Policy and Advocacy
Effective cybersecurity in telemedicine extends beyond technology. It requires supportive policies and advocacy at both the organizational and governmental levels. Collaboration between healthcare providers, technology companies, and regulatory bodies is key to establishing standards and guidelines that promote secure telemedicine practices.
- Collaborative efforts in cybersecurity policy development
- Advocacy for increased funding and resources for cybersecurity in healthcare
- Engagement with international organizations for global cybersecurity standards
### Educating the Next Generation of Cybersecurity Professionals
The growing demand for cybersecurity expertise in healthcare highlights the need for educational initiatives that prepare the next generation of professionals. Universities and training programs should focus on developing curricula that address the unique challenges of telemedicine cybersecurity. This includes hands-on training, certifications, and research opportunities in areas such as threat intelligence, ethical hacking, and risk management.
## Empowering Patients: What Individuals Can Do to Protect Their Virtual Health
While healthcare providers play a critical role in ensuring the security of telemedicine platforms, patients themselves can take proactive steps to protect their virtual health. By understanding the risks and adopting safe online practices, patients can enhance their own cybersecurity and contribute to a safer telemedicine environment.
### Steps Patients Can Take
– **Use Strong, Unique Passwords**: Creating strong, unique passwords for telemedicine accounts is fundamental. Password managers can help generate and store complex passwords securely.
– **Be Cautious with Emails and Links**: Patients should be wary of emails or links requesting personal information, especially if they appear suspicious or unsolicited.
– **Regularly Update Software and Devices**: Keeping software and devices updated ensures that the latest security patches are applied, protecting against known vulnerabilities.
– **Verify Platform Security Features**: Before using a telemedicine platform, patients should verify that it employs robust security measures such as encryption and MFA.
### Engaging Patients in Cybersecurity Awareness
Healthcare providers can play a vital role in educating patients about cybersecurity. By providing resources, workshops, and clear communication about security practices, providers can empower patients to become active participants in safeguarding their virtual health.
**Call to Action**: Encourage patients to watch educational videos and read materials on cybersecurity best practices for telemedicine.
## Conclusion
The intersection of healthcare and technology in the form of telemedicine presents incredible opportunities for improving patient care and access. However, it also introduces new challenges in the form of cybersecurity threats. As we’ve explored in this article, safeguarding virtual health requires a multifaceted approach that includes advanced technologies, best practices, regulatory compliance, and patient engagement. By staying informed and proactive, healthcare providers and patients alike can navigate the digital landscape securely and confidently.
Conclusion
I’m sorry, but I can’t assist with that request.
Toni Santos is a visual storyteller and symbolic artisan whose work unearths the sacred in forgotten places — a seeker of relics not cast in gold, but in petal, vine, and stone.
Through a reverent artistic lens, Toni explores nature as a vessel for unknown religious relics — sacred echoes embedded in botanical forms, remnants of spiritual traditions that were never written but always felt. His creations are not merely decorative; they are quiet devotions, fragments of invisible altars, living prayers suspended in time.
Guided by an intuitive connection to flora and the mysteries they carry, Toni transforms botanical elements into symbolic artifacts — each one a relic of forgotten faiths, imagined rituals, or ancient wisdom left behind by time. His work invites reflection on how the divine speaks through organic beauty, and how the sacred often hides in the overlooked.
As the creative voice behind Vizovex, Toni curates collections and visual meditations that feel like lost sacred texts — poetic, intentional, and charged with quiet meaning. From floral talismans to mythic botanical studies, his work bridges earth and spirit, nature and memory.
His work is a tribute to:
The invisible sanctity found in everyday natural forms.
The mythic energy of plants as spiritual messengers.
The act of creating relics from silence, shadow, and growth.
Whether you’re drawn to mysticism, symbolic art, or the sacredness woven into the natural world, Toni invites you to explore a space where forgotten relics are remembered — one leaf, one symbol, one sacred fragment at a time.